Massive transfusion in trauma - a literature review.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58951/dataset.2024.003Keywords:
Hemorrhagic shock, Transfusion Protocols, Polytrauma care, Antifibrinolytic, CalciumAbstract
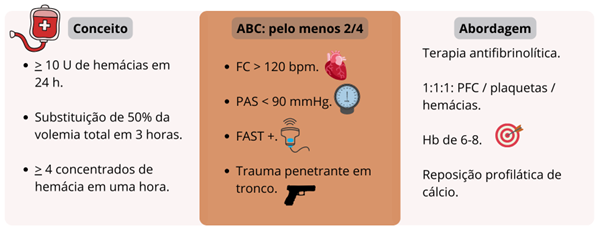
Massive transfusion is defined as the transfusion of at least 10 units of red blood cells concentrate within 24 hours. Although most commonly used in the context of cardiac and vascular surgery, severe hemorrhagic trauma is its classic indication and the scenario in which the strategy is most studied. The decision to initiate the massive transfusion protocol requires consideration, as it is as important as offering an early response to shock, as it is to avoid complications related to the unnecessary use of blood products. Therefore, it is extremely important to properly select patients who will benefit most, which can be aided by scores such as the Assessment of Blood Consumption. Other criteria for starting the massive transfusion protocol include persistent hemodynamic instability, active bleeding requiring surgery or angioembolization and blood transfusion at the scene. In this context, it is important that the emergency professional is familiar not only with the indications for massive transfusion, but also with the technical aspects and adjuvant measures..
References
American College of Surgeons - ACS. (2014). ACS TQIP Massive Transfusion in Trauma Guidelines. American College of Surgeons (ACS).
American College of Surgeons - ACS. (2018). ATLS Advanced Trauma Life Support 10th Edition Student Course Manual (10th ed.). ACS American College of Surgeons.
Ditzel, R. M., Anderson, J. L., Eisenhart, W. J., Rankin, C. J., DeFeo, D. R., Oak, S., & Siegler, J. (2020). A review of transfusion- and trauma-induced hypocalcemia: Is it time to change the lethal triad to the lethal diamond? Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 88(3), 434–439. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000002570
Dorken Gallastegi, A., Naar, L., Gaitanidis, A., Gebran, A., Nederpelt, C. J., Parks, J. J., Hwabejire, J. O., Fawley, J., Mendoza, A. E., Saillant, N. N., Fagenholz, P. J., Velmahos, G. C., & Kaafarani, H. M. A. (2022). Do not forget the platelets: The independent impact of red blood cell to platelet ratio on mortality in massively transfused trauma patients. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 93(1), 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000003598
Fundação Hospitalar de Hematologia e Hemoterapia do Amazonas - HEMOAM. (2023). Manual de transfusão sanguínea (S. R. Lopes & Albuquerque (eds.)). HEMOAM.
Goodman, M. D., Makley, A. T., Hanseman, D. J., Pritts, T. A., & Robinson, B. R. H. (2015). All the bang without the bucks: Defining essential point-of-care testing for traumatic coagulopathy. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, 79(1), 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000000691
Hess, J. R. (2023). Massive blood transfusion. UpToDate. Accessed on 06 June 2024. Available at: <https://www.uptodate.com/contents/massive-blood-transfusion?search=Massive%20blood%20transfusion>
Liu, Z., Ayyagari, R. C., Martinez Monegro, E. Y., Stansbury, L. G., Arbabi, S., Bulger, E. M., Vavilala, M. S., & Hess, J. R. (2021). Blood component use and injury characteristics of acute trauma patients arriving from the scene of injury or as transfers to a large, mature US Level 1 trauma center serving a large, geographically diverse region. Transfusion, 61(11), 3139–3149. https://doi.org/10.1111/trf.16679
Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro - UFTM. (2023). Protocolo EBSERH. Manejo de Pacientes Adultos em Transfusão Maciça. EBSERH.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Luís Gustavo Rodrigues Barbosa, Maurício Moraes Assis

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal publishes its Open Access articles under a Creative Commons license (CC BY 4.0).
You are free to:
Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format for any purpose, even commercially.
Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation.
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.




